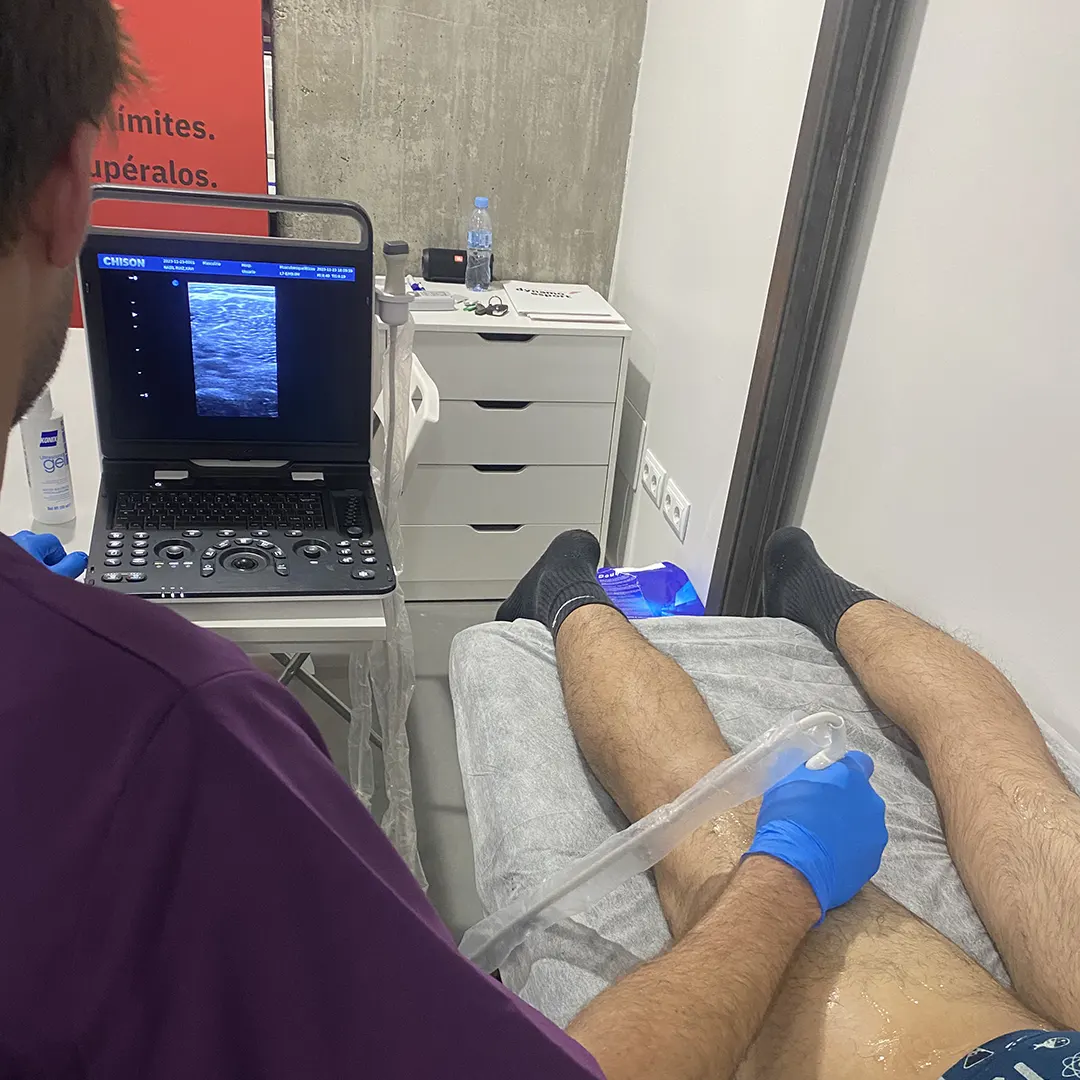
— Musculoskeletal ultrasound
What is musculoskeletal ultrasound?
It’s a technique that uses ultrasound waves to create images of muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
Musculoskeletal ultrasound is increasingly used in clinical practice, both for diagnosis and for monitoring the progression of a condition. This is because it is a non-invasive, non-ionizing test that is painless, safe, immediate, and dynamic.
What is musculoskeletal ultrasound used for?
Musculoskeletal ultrasound is used to diagnose conditions affecting muscles, joints, and tendons.
It’s an effective tool that allows for the objective assessment of injured tissue, enabling the planning of appropriate and thus more effective treatment.
What do we typically assess in our field?
-
-
- Muscle: Abnormalities secondary to trauma (tears, hematomas…) and their complications or sequelae; inflammatory processes and/or focal masses.
- Tendons: Suspected partial or complete tears, inflammation, and subluxation or dislocation.
Bursitis: Secondary to trauma. - Peripheral nerves: Suprascapular nerve (identify ganglion); sciatic and median nerves. Palpable focal masses: Schwannomas, neurofibromas.
-
What is musculoskeletal ultrasound?
It’s a technique that uses ultrasound waves to create images of muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
Musculoskeletal ultrasound is increasingly used in clinical practice, both for diagnosis and for monitoring the progression of a condition. This is because it is a non-invasive, non-ionizing test that is painless, safe, immediate, and dynamic.
What is musculoskeletal ultrasound used for?
Musculoskeletal ultrasound is used to diagnose conditions affecting muscles, joints, and tendons.
It’s an effective tool that allows for the objective assessment of injured tissue, enabling the planning of appropriate and thus more effective treatment.
What do we typically assess in our field?
-
-
- Muscle: Abnormalities secondary to trauma (tears, hematomas…) and their complications or sequelae; inflammatory processes and/or focal masses.
- Tendons: Suspected partial or complete tears, inflammation, and subluxation or dislocation.
Bursitis: Secondary to trauma. - Peripheral nerves: Suprascapular nerve (identify ganglion); sciatic and median nerves. Palpable focal masses: Schwannomas, neurofibromas.
-
Echocardiography
Echocardiography is an ultrasound examination used to assess the heart’s structure and function. It helps diagnose heart conditions, such as valve issues, heart failure, congenital malformations, and more. This non-invasive procedure provides detailed images of the heart and its tissues, allowing for the evaluation of a patient’s cardiovascular health.